Guide to Google Ranking Factors: How to Improve Your SEO Strategy
Welcome to Part I of a six part series serving as your guide to Google ranking factors
The internet is a channel to reach countless customers and build brand awareness. Theres’s online advertising, social media, content marketing, influencers and affiliates to name only a few. Each has its benefits but we believe a strong Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy is one of the most cost effective and highly converting channels to communicate with your customers.
Developing and implementing an SEO strategy requires understanding certain key subjects, including Search Engine Results Page (SERP), general SEO concepts, and the way in which Google’s algorithm impacts where your content ranks in Google searches.
This guide will introduce you to these basics. Even if you think you’re already familiar with SEO best practices, you’ll still find valuable information here. After all, Google’s algorithm often changes. Best practices applied in the past may no longer be useful today. Additionally, you may overlook the important role new factors can play in an SEO strategy’s effectiveness if you don’t consistently research new developments.
The information here will help both beginners and seasoned marketers better understand essential topics. Apply these lessons when developing your SEO strategy for optimal results.
Introduction to SERPs
A Search Engine Result Page, or SERP, is exactly what it sounds like: a page displaying the results of an online search. Although there are multiple search engines currently in use, this guide will focus primarily on Google, which has a 75% market share and is thus by far the most popular search engine on the planet.
Your goal is to rank high on SERPs. According to one survey, 75% of internet users don’t even check the second page of search results. Ranking high on page 1 is key to getting noticed.
However, it is by no means the only important factor. Over the years, Google has added new features to its SERPs.
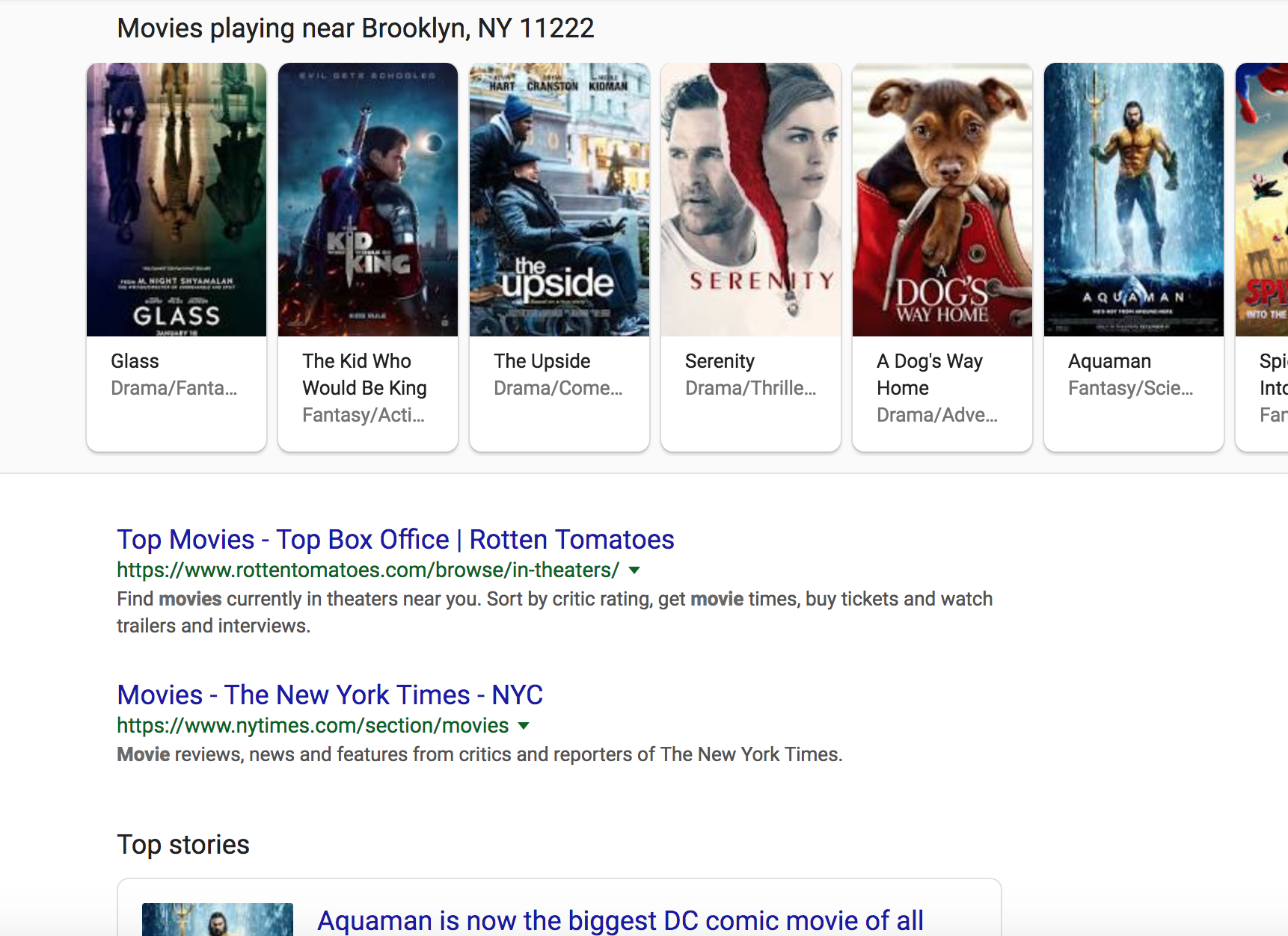
There was a time when Googling the word “movie” would yield a mix of results (sites for movie reviews, movie times, movie theaters), all of which would be presented in a relatively similar manner. That’s no longer the case. Look at the SERP page for that search now:
This is just a small portion of the SERP. As you can see, searching for “movie” delivers several different types of results. There is a list of movies playing near the user’s current location, a couple of websites, and a news story.
This type of result isn’t uncommon. The features on display, however, will change depending on the nature of a search. For instance, if you were to search “taco,” Google would likely display a small map of nearby taco restaurants, among other features.
The following are specific SERP features worth understanding if you want to optimize your SEO strategy:
- Snippets: Snippets are the format most people typically expect search results to appear as. They feature the name of the page, the meta-description, and the URL. However, some results may be displayed as “rich snippets.” These display additional content. The specific type of content they include may vary depending on the nature of the search result. For instance, a search that yields a product page might result in a snippet which displays a five-star ranking from other customers. The link above explains how to incorporate data on your page to help Google create a rich snippet.
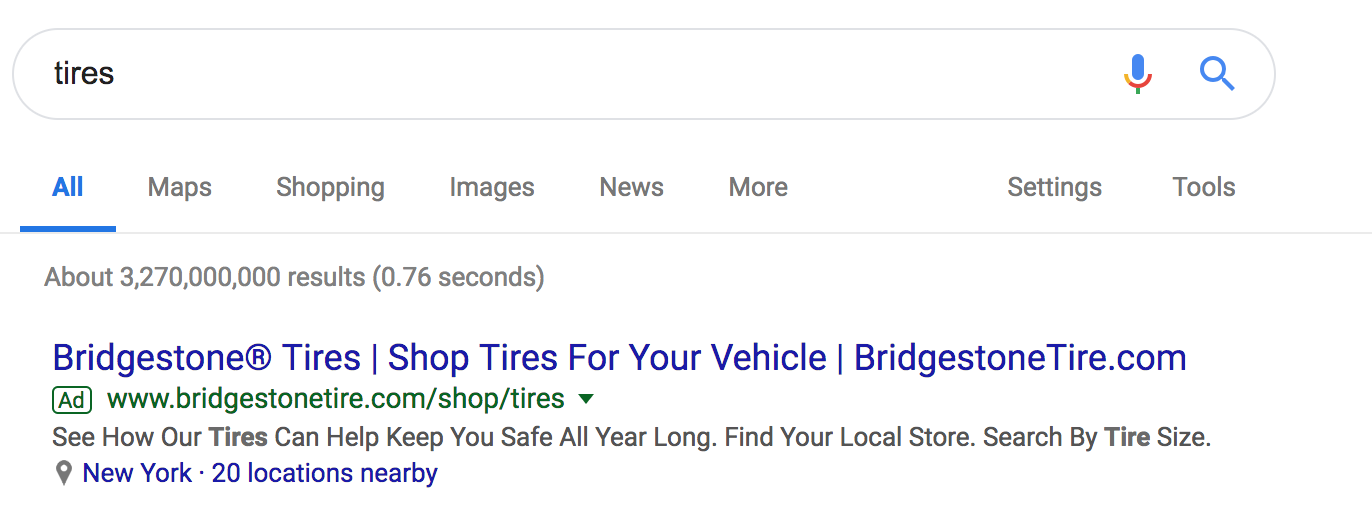
- Google Ads: Typically displayed above or below organic search results, paid results or Google Ads are simply results marketers have paid for by bidding on keywords. Google will label them accordingly to ensure anyone browsing understands when a particular result is an ad.
- Universal Results: Depending on the nature of a search, a Google SERP might also display some results from other types of searches. For instance, if someone were to Google the word “sunset,” a few pictures might appear above the text-based results to give a user a sense of what they might find if they were to perform a Google Image search with that word.
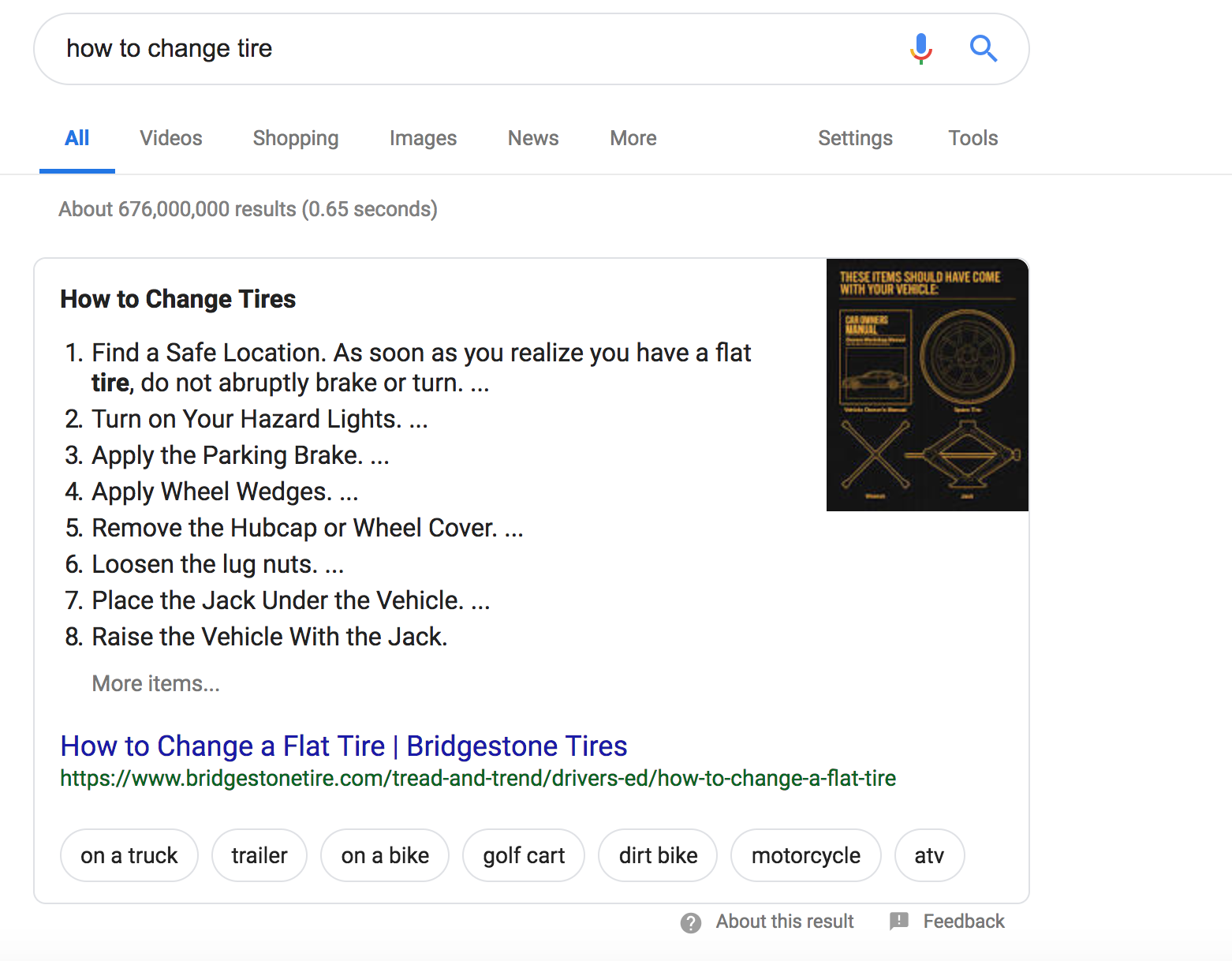
- Featured Snippet: Sometimes a result answers a user’s question so perfectly Google’s SERP displays a larger than average snippet with additional content from the actual page.
These images illustrate what various types of snippets look like. Rich snippet:
Featured Snippet:
Google Ads:
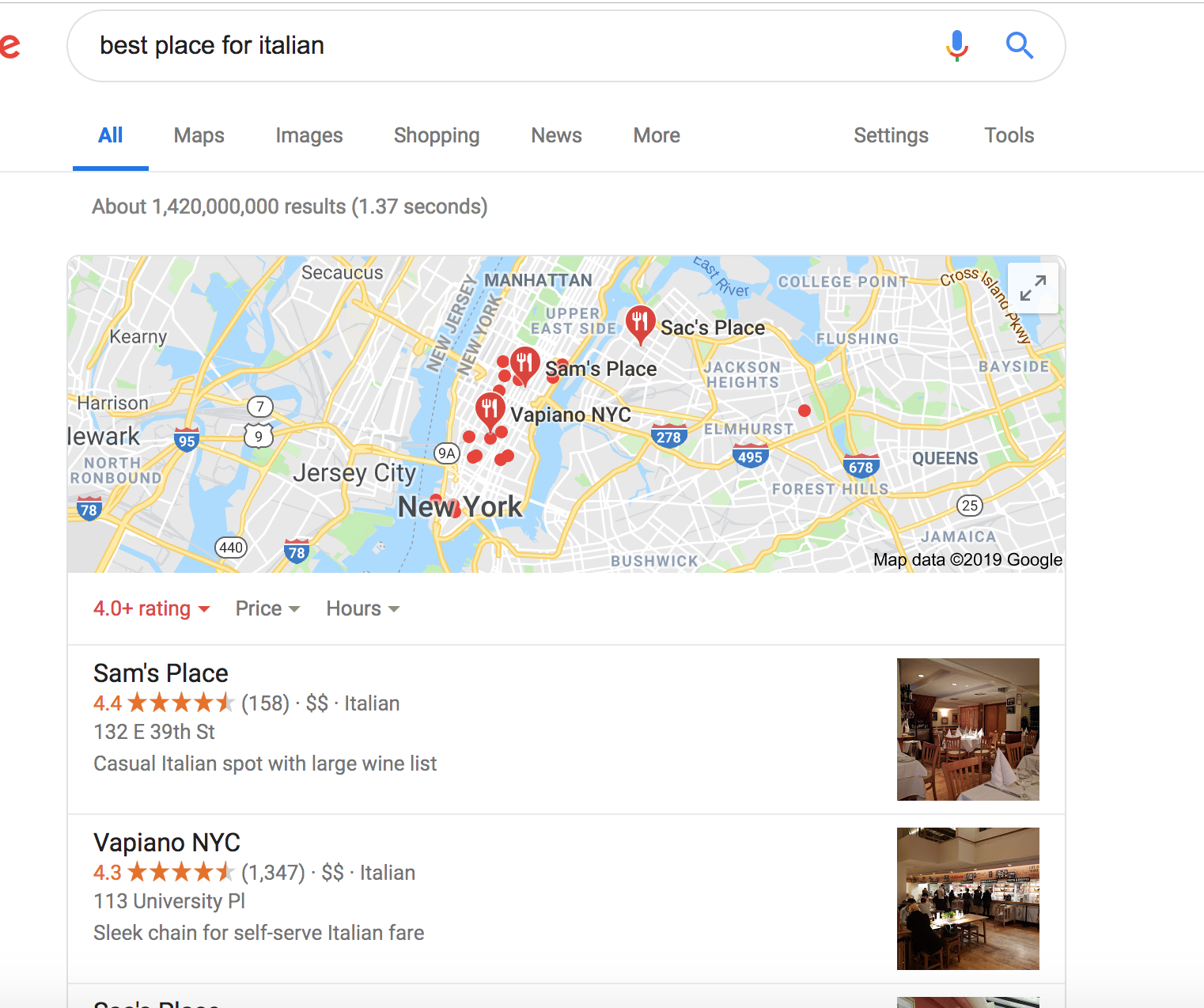
Although there are many other features on Google SERPs, from shopping results to business pages, these are the most relevant to your needs from an SEO perspective. To use an example that we’ll revisit later, consider the results you get if you search “best places for Italian”:
Searching “best place for Italian” yields results displaying nearby Italian restaurants. There’s a reason Google understands this is what a person is searching for, there’s a reason the results are displayed in this manner, and there’s a reason the results will differ based on the context of the search, all of which you’ll learn about later in this guide.
Introduction to SEO
Search engine optimization, or SEO, involves understanding how numerous factors impact the likelihood that internet users will find your content when performing relevant searches. Again, because SEO best practices are constantly changing, it’s important to consistently research this topic to ensure your strategy doesn’t need to be adjusted.
SEO is valuable because it has the potential to yield a major return on investment by helping new followers find your website. This is very important if you run a business. Quite simply, the more people visit your site, the more money you’ll make. Investing in a proper SEO strategy helps you attract that kind of attention.
However, SEO can be complicated. Google currently uses greater than 200 ranking factors when determining where a page will appear in SERPs. Covering all of those factors here would be impossible. Instead, it’s best to focus on these specific examples, which we will cover later in this guide. In this section, however, you will learn about the basic types of factors impacting your SEO. To understand them, you first need to understand how Google’s algorithm works.
What You Need to Know About Google’s Algorithm
User intent is very important when determining what to display on SERPs. There are many reasons this is the case. For example, sometimes two words can have very different meanings depending on the situation. An “apple” is a fruit, but it’s also the name of a major tech company. It’s important for an algorithm to accurately “understand” a user’s intent when they performing a search.
That’s why both RankBrain and Hummingbird significantly improved online searches for many internet users. The following overviews explain how:
Hummingbird
Hummingbird was officially announced in September of 2013, although it had been in use for a month by that point. To understand the manner in which it improved search, let’s return to the example from earlier:
How does Google determine these results are most likely to match what the person performing the search was looking for? How does an algorithm know the person performing this search intended to specifically find Italian restaurants (when neither the word “food” nor “restaurant” appeared in the query)? Why not assume they were looking for the best places for Italian fashion design, or the best places for Italian people to live? Yes, the average person generally understands what you are asking for when you ask about “best places for Italian,” but does an algorithm?
To a degree, yes. That is the primary function of Hummingbird: to understand semantic search with the goal of providing users a more human experience.
Prior to Hummingbird’s release, finding exactly what you were looking for via a search engine wasn’t always easy. You needed to carefully choose the correct combination of words to get the results you sought. The algorithm didn’t understand much of the nuance of natural human language. Again, you could have performed searches that resulted in SERPs containing irrelevant links simply if your search featured a word with multiple meanings. This had an impact on SEO strategy in many ways. Marketers and companies often published content that didn’t sound human, as keywords were awkwardly forced in places they might not have belonged.
Hummingbird changed that. It’s designed to understand conversational searches to better determine a user’s intent. In fact, some suspect its development and release was an early step in the direction of voice search for Google. Innovations such as natural language processing made this possible.
RankBrain
RankBrain is another improvement designed to better identify a user’s specific intent when they perform searches. Instead of merely using a traditional algorithm to determine relevant search results, RankBrain essentially “interprets” the search by applying various other factors (from location to presumably search history) in order to fully understand what a user is looking for.
It achieves this by using machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence. RankBrain is particularly effective as a means of contextualizing a search.
A basic example would be the previous search for “best places for Italian.” The context of that search is someone sitting in Brooklyn, New York. For someone in California, the context is different, and thus the results will be different.
Again, that’s a very basic example. The true value of RankBrain lies in its ability to understand more complicated searches that may not be common. The AI helps the algorithm learn to connect these searches to common ones by analyzing how other users behaved using similar keywords.
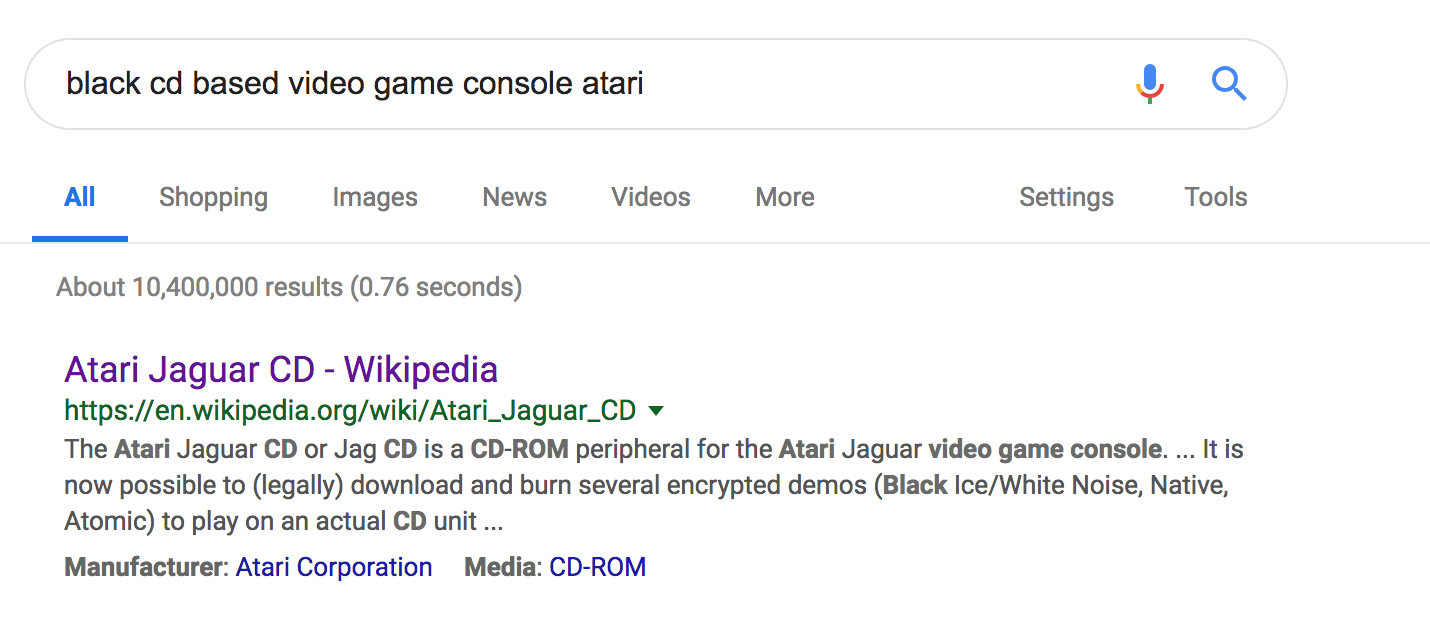
For example:
That’s a very specific and relatively unique search. However, the first result is correct. Someone performing this search would be trying to remember the name of a video game console that was black, made by Atari, available in the 90s, and used CDs instead of cartridges. RankBrain helps Google’s algorithm shift away from looking for pages which contain these words together in sequence, instead focusing on correctly identifying a searcher’s intent through data analysis.
Of course, traditional factors still impact your rank. General categories of important ranking factors are website factors, domain factors, page factors, backlink factors, and user factors.
Website Factors
Well-organized website architecture helps Google better understand what type of content is available on a given page. For instance, if you ran a site reviewing local restaurants, you might want to organize your reviews into different subcategories based on cuisine.
User behavior has an affect on SEO. The easier it is for visitors to find the content they’re looking for on your site, the better it will rank.
Domain Factors
Various domain factors impact your rank, including domain age (older sites typically rank higher) and security. Additionally, stuffing keywords into a domain name could have a negative impact on your rank.
Page Factors
Page factors such as load time, content quality, keyword density, and numerous others also impact SEO. A page boasting relatively strong content that nevertheless loads slowly will rank lower than an otherwise equally strong page that loads quickly.
Backlinks
Creating and publishing high-quality content should be an essential component of any SEO strategy. There are many reasons this is is the case. The fact that you’ll receive more backlinks is one of them. A backlink is simply a link from a different site directing a user to your page. As you acquire more backlinks, Google will determine you must be an authority on this particular subject. This will improve your ranking in SERPs.
User Factors
Again, the way in which users interact with your content is very important to Google’s algorithm. For instance, if users who click on a page in a SERP often click away from it quickly after doing so, Google’s algorithm may read this as the page not offering the type of content people are looking for when they perform that specific search. Of course, sometimes a high bounce rate simply means your content is short, and presented in such a way that users can find the answers to their questions without spending much time on your page. This is a reason including longform content in your SEO strategy is a smart idea.
Another user factor would be your CTR, which refers to the rate at which people actually click on a link to your page when they find it in SERPs. The higher your CTR, the higher your ranking will typically be.
The remainder of this guide will explore these various types of factors in greater detail. By understanding how they impact your SEO, you can better understand how to develop a strategy that yields the best possible results.